If you’re wondering which appliances use the most electricity at home, heating and cooling devices are usually top of the list.
Electrical appliances like showers, ovens, tumble dryers and heaters can all consume massive amounts of energy - but they’re not the only culprits. That’s why we’re going to show you exactly how much electricity each of your home appliances use, so you can be more energy efficient and reduce the cost of your electric bill.
Top 20 biggest users of electricity in the home
Now that we’ve introduced the usual suspects, let’s break down the biggest electricity users in your home. They fall under the following categories:
- Heating Appliances
- Cooling Appliances
- Laundry and Washing Appliances
- Cooking Appliances
- Electronics Appliances
- Lighting Appliances
Before we look at specific appliances, it’s important to understand two key things that affect how much electricity an appliance uses:
- Energy Rating - This is how much power (in watts or kilowatts) an appliance uses per hour. The higher the rating, the more electricity it needs.
- Time Usage – This is how long the appliance is switched on each day. More hours mean more energy used.
Taking both these factors into account, we’ve calculated the typical daily energy use of common home appliances, and added a "£" rating to show which cost the most to run.
Function | Appliance | Energy Rating (kW) | Daily Use (hrs) | kWh/day | £ Rating |
Heating Appliances | Electric Shower | 10.0 | 0.5 | 5.0 | £££ |
Electric Heater | 2.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 | £££ | |
Cooling Appliances | Fridge Freezer | 0.4 | 24.0 | 0.75 | ££ |
Extractor Fan | 0.01 | 0.5 | 0.005 | £ | |
Laundry & Washing Appliances | Tumble Dryer | 2.5 | 1.0 | 2.5 | £££ |
Washing Machine | 1.5 | 0.75 | 1.2 | ££ | |
Hair Dryer | 1.5 | 0.15 | 0.23 | £ | |
Vacuum Cleaner | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.07 | £ | |
Cooking Appliances | Oven | 2.2 | 1.0 | 2.2 | £££ |
Electric Hob | 1.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | ££ | |
Air Fryer | 1.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | ££ | |
Kettle | 2.7 | 0.25 | 0.7 | ££ | |
Dishwasher | 1.2 | 2.0 | 2.4 | £££ | |
Electronics Appliances | TV | 0.2 | 3.0 | 0.6 | ££ |
Games Console | 0.2 | 2.0 | 0.4 | ££ | |
Broadband Router | 0.01 | 24.0 | 0.24 | £ | |
Desktop Computer | 0.14 | 8.0 | 1.12 | ££ | |
Printer | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | £ | |
Phone Charger | 0.01 | 7.0 | 0.07 | £ | |
Lighting Appliances | Lightbulbs | 0.01 | 5.0 | 0.05 | £ |
You can easily adapt the figures above to reflect your own daily usage and appliances. Just use this simple formula:
kWh/day × unit price on your electricity tariff = daily running cost.
Are you on the right electricity plan?
Once you've worked out how much your appliances are costing, it's worth checking if you're on the best tariff for your home. At Power NI, we're committed to helping households across Northern Ireland to get more from their electricity plans. That's why we offer the best possible energy prices and a range of options.
Compare Our Electricity Plans & Prices
Energy usage of heating appliances

Heating appliances might not be switched on all day, but when they are, they use a lot of electricity. Showers and heaters are two of the biggest users — especially in winter when we rely on them the most.
-
How much electricity does an electric shower use?
An electric shower typically uses between 7.5 kW and 10.5 kW of electricity per hour, making it one of the most energy-hungry appliances in the home. Its saving grace is that the average time spent in the shower is eight minutes — but this can start to add up for larger households.
You can use less electricity by:- Setting a timer on your phone for the time you want to spend in the shower.
- Switching to an energy-efficient aerated shower head, which will use less water and need less electricity to heat the water.
- Turning the shower off when lathering or shampooing, and switching it back on to rinse.
-
How much electricity does a blow heater use?
A blow heater typically uses between 1 kW and 2 kW of electricity per hour, depending on the model. These are great if you’re to quickly warm up a small space, but the energy they use can add up if they’re left running for long periods.
You can use less electricity by:- Choosing the lowest possible setting — many blow heaters have a choice of heat outputs.
- Setting timers to make the room comfortable when you arrive.
- Switching to a heat pump for a more energy-efficient way to heat your home long-term.
Energy usage of cooling appliances

Cooling appliances tend to run quietly in the background — but that also means they’re using electricity around the clock. With more households in the UK now owning multiple cooling devices, including a growing number of freezers, the energy impact can be higher than you might expect.
-
How much electricity does a fridge freezer use?
Fridge freezers typically use between 200 kWh and 500 kWh of electricity every year. Although they are plugged in 24 hours a day, they don’t work at full power all the time and only use as much energy as they need to maintain the right temperature.
You can use less electricity by:- Choosing an energy-efficient, A-rated fridge freezer.
- Operating your fridge below 5°C and your freezer at -18°C.
- Keeping your fridge about three-quarters full to improve air circulation.
-
How much electricity does an extractor fan use?
Extractor fans typically use between 5 and 40 watts per hour. For example, a standard bathroom fan running for 30 minutes a day would use around 15 kWh of electricity per year — a very low amount compared to most household appliances.
You can use less electricity by:- Opening windows to increase ventilation in your bathroom.
- Using a modern extractor fan with a more efficient motor.
- Choosing an extractor fan that has a sensor that helps it to adapt the amount of energy used based on moisture levels in your bathroom.
Energy usage for laundry and washing appliances
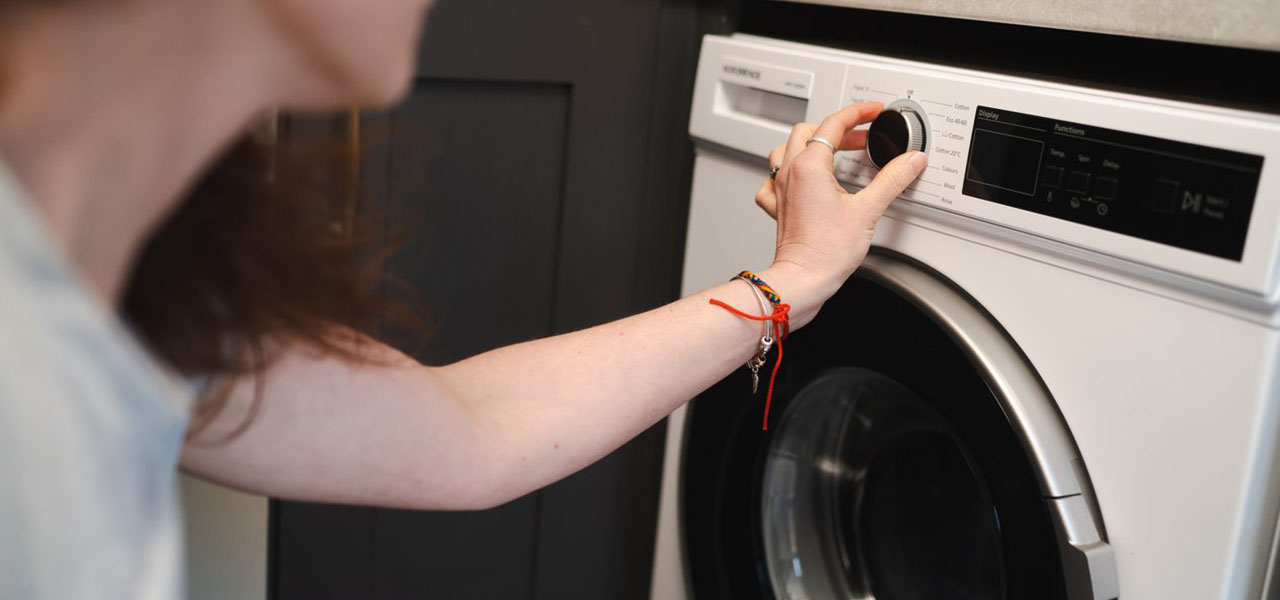

We all need clean clothes and clean homes — but it doesn’t come free! Washing machines and dryers are some of the most widely owned major appliances worldwide, and they use more electricity than you might think. Let’s take a look at how much.
-
How much electricity does a tumble dryer use?
Tumble dryers can use anywhere from 2 to 5.3 kWh of electricity per full load, depending on the type. Heat pump dryers are the most energy-efficient, using around 2.1 to 2.5 kWh, while condenser and vented models typically use between 5.2 and 5.3 kWh per load.
You can use less electricity by:- Giving clothes an extra spin cycle to get rid of excess moisture
- Untangling bundled clothes and cleaning the lint filter after each cycle so that air can circulate better.
- Air drying clothes outside whenever possible.
-
How many watts does a washing machine use?
Washing machines use between 400 and 2,100 watts, depending on the size, model and cycle settings. Smaller, compact washing machines might use around 500 to 800 watts, while large or high-efficiency models can draw up to 2,100 watts at peak.
The actual power used during a wash varies based on the temperature, spin speed and load size — but on average, a full cycle uses between 0.5 and 2.5 kWh of electricity.
You can use less electricity by:- Wash your clothes at the lowest possible temperature.
- Only using your washing machine when you have a full load ready.
- Choosing an energy-efficient, A-rated washing machine
-
How much electricity does a hair dryer use?
Hair dryers generally use between 800 and 2,000 watts of electricity, depending on the setting used. If you use a hair dryer for around 10 minutes a day, it will use about 0.25 to 0.33 kWh per day, or roughly 7.5 to 10 kWh per month. Because they’re only on for short periods, the overall energy use stays relatively low.
You can use less electricity by:- Towel drying your hair first.
- Unplugging your hair dryer when it’s not in use.
- Choosing a low-wattage hair dryer.
-
How much electricity does a vacuum cleaner use?
Vacuum cleaners are not major users of energy in our homes. Most vacuum cleaners have an energy rating of between 0.6 kW and 0.9 kW. With a vacuum cleaner only in use 30 minutes per week on average, the costs of keeping your carpets clean are very low.
You can use less electricity by:- Upgrading to a modern vacuum cleaner — newer models are more energy-efficient.
- Using a vacuum that gets dust up more quickly so you don’t have to use it for as long.
- Emptying your vacuum cleaner before it gets two-thirds full to maintain efficiency.
Energy usage for cooking appliances
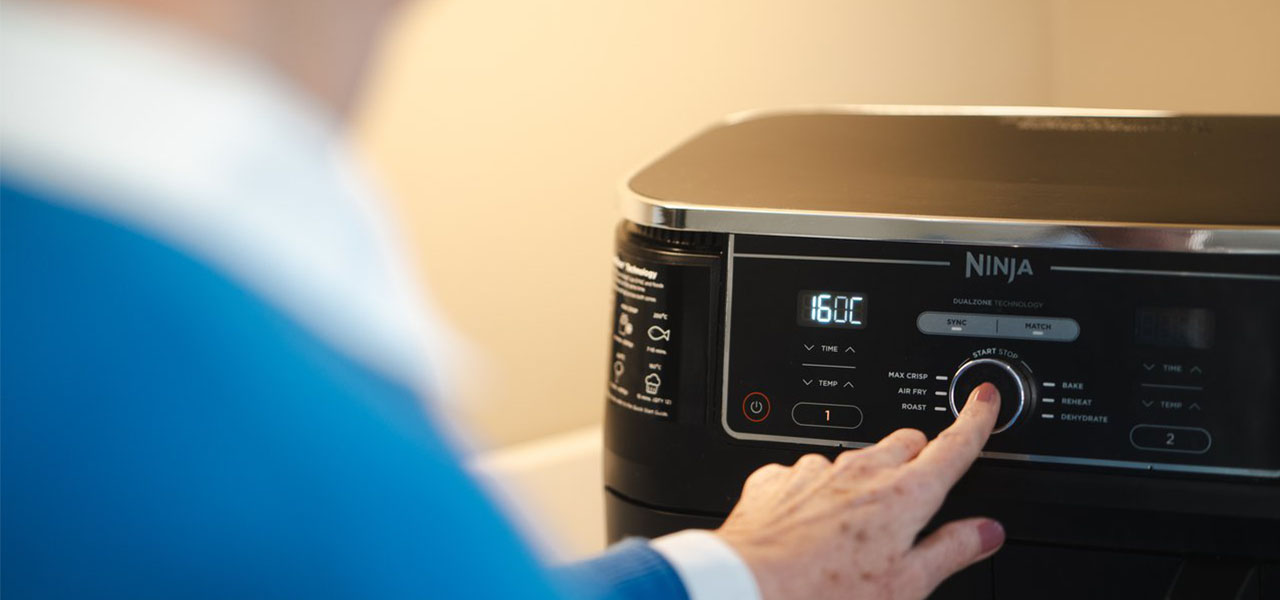

Cooking appliances are some of the hardest workers in the home. Whether you're making meals from scratch or just boiling the kettle, the energy used in the kitchen can quickly stack up.
-
How much electricity does an oven use?
An electric oven can be one of the most expensive appliances to run in your home. Electric ovens usually have an energy rating of between 2 kW and 2.4 kW, and will typically be in use for an hour each day.
You can use less electricity by:- Swapping to a slow cooker or air fryer - both are far more efficient.
- Using a microwave where possible.
- Keeping the oven door closed when it’s in use to stop heat from escaping.
-
How much electricity does a hob use?
An electric hob will typically use about 0.75 kWh of energy per use. Most electric hobs have an energy rating of around 1.5 kW — a fairly energy-hungry figure — and will normally be on for around half an hour.
You can use less electricity by:- Boiling water in the kettle first instead of heating cold water on the hob.
- Put a lid on your pans to get them up to temperature more quickly.
- Using an air fryer, which is more energy-efficient, to replace your frying pan.
-
How much electricity does an air fryer use?
Air fryers are becoming a staple in many kitchens thanks to their speed and energy efficiency. Most air fryers use around 1000W (1kW) to 1800W (1.8kW), which is similar to an electric hob — but because they cook food faster, they often use less energy overall.
You can use less electricity by:- Using the air fryer instead of your oven for smaller meals.
- Avoiding unnecessary preheating — many models don’t need it.
- Cleaning the basket and fan regularly to keep it running efficiently.
-
How much electricity does a kettle use?
Kettles usually have one of the highest energy ratings of all household appliances. Fortunately, we only ever need it for a few minutes at a time so the energy costs of a cup of tea or coffee don’t get too high.
You can use less electricity by:- Only using as much water as you need, a half-full kettle uses half as much energy.
- Using a kettle with a low minimum fill level so you can boil just enough water for one cuppa.
- Choosing an insulated kettle, which will boil more quickly.
-
How much electricity does a dishwasher use?
Dishwashers are another of the most energy-hungry appliances in our homes. They are typically energy rated between 1.2 kW and 2.4 kW. With programmes lasting up to three hours in some cases, that can start to add up.
You can use less electricity by:- Waiting until the dishwasher is full before putting it on.
- Choosing a lower temperature or ‘eco’ programme.
- Putting your dishwasher on overnight if you’re on an economy 7 plan.
Energy usage for electrical appliances
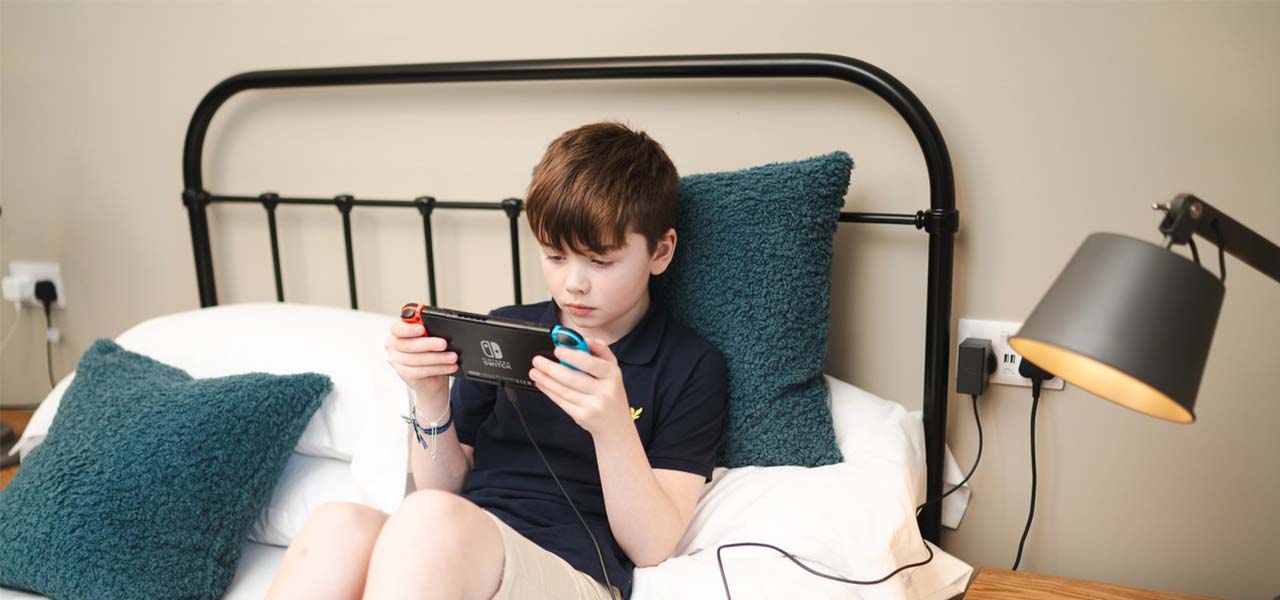

From movie nights to working from home, we rely on electronics more than ever. TVs, consoles, routers and computers might seem low-cost to run individually — but with more devices in use for longer each day, the total energy use can add up fast.
And with UK households spending more each year on small electrical appliances, the impact on your bill might be more than you'd expect.
-
How much electricity does a TV use?
An LCD TV uses around 0.2 kW per hour on average. That’s not very much but it can start to add up if the TV is on for long periods. And the bigger your screen, the more energy it will use.
You can use less electricity by:- Choosing a TV that is only as big as you need it to be.
- Switching off at the wall and not leaving your TV in standby mode.
- Selecting eco or energy-saving mode and turning down the brightness on your TV.
-
How much electricity does a games console use?
Games consoles don’t use much electricity. Consoles are usually energy rated at between 0.1 kW and 0.2 kW so even during extended gaming sessions, they won’t run up too much of a bill.
You can use less electricity by:- Switching consoles off at the wall when not in use and not leaving them in standby.
- Checking your console’s settings for energy-saving modes.
- Setting a timer for how long you want to spend using your console.
-
How much electricity does a broadband router use?
Broadband routers use between 2 and 20 watts an hour to run. The average energy consumption for a router is 6 watts an hour. This is very low but it’s likely to be a cost that’s running around the clock.
You can use less electricity by:- Switching the router off when you’re away.
- Keeping the router dust-free and well-ventilated to avoid overheating.
- Swapping from a router with higher energy consumption.
-
How much electricity does a desktop computer use?
Regular use of a desktop computer will have a noticeable impact on your energy bills. Energy ratings of between 0.1 kW and 0.2 kW make computers similar to TVs for energy use. This adds up if a desktop computer is on for eight hours a day, five days a week.
You can use less electricity by:- Not leaving your computer in standby mode overnight — switch it off at the wall.
- Switching off your screen when stepping away from your desk for a short time.
- Swapping to a laptop or tablet when possible.
-
How much electricity does a printer use?
Printers have fairly low energy usage, and rarely cost much to run because they are not in constant use. A printer might use around 50 watts when printing, 2 watts in standby mode and 1 watt in sleep mode.
You can use less electricity by:- Only switch the printer on when you need to use it.
- Turning the printer off at the wall when it’s not in use.
- Choosing eco, quick or draft quality print settings when appropriate.
-
How much electricity does a phone charger use?
A phone charger uses between 2 watts and 10 watts an hour when charging your phone. It will use some electricity — but no more than 0.5 watts — when plugged in but not connected to your phone.
You can use less electricity by:- Charging your phone during the day instead of leaving it plugged in overnight.
- Unplugging your charger when it’s not in use.
- Closing unused apps, turning down screen brightness and using power-saving modes to make each charge last longer.
Energy usage for lighting appliances

Most of the time we don't think twice about flipping on a light. But when you add up every bulb in the house, lighting can still make a dent in your electricity use.
-
How much electricity do lightbulbs use?
Low-energy lightbulbs use as little as 18 watts an hour. They can be 90% more efficient than standard light bulbs. That can add up to a huge difference in electricity costs over time.
You can use less electricity by:- Swapping all standard light bulbs to low-energy bulbs, and prioritising energy-efficient lighting.
- Using lamps rather than big lights when possible.
- Always turning lights off when you leave a room.
Worst appliances to leave on standby
Leaving appliances in standby mode is a waste of energy and pushes up your energy bills with absolutely no benefit to you. Is your home full of vampire devices that are guzzling up electricity without you even realising it?
These are some of the worst appliances to leave on standby.
Top 5 energy-intensive appliances

Television
You could save up to £49.22 a year by waving goodbye to the little red light and switching your TV properly.

Television box
When you switch off the TV, don’t forget your set-top box. You could save an extra £46.20 by switching it off.
Microwave
If it’s still got an LED display, it’s still using power. Turning your microwave off at the wall could save £32.74 a year.

Games Console
Switching off a games console instead of leaving it in standby mode will save you around £24.34 a year.
Electric shower
Do you remember to pull the cord when you’re finishing in the shower? You’ll save around £19.60 a year if you do.
Save money on energy-efficient appliances with Power NI Perks
If you’ve spotted an appliance that’s costing more than expected, it might be time for an upgrade — and we’re here to help.
Power NI customers can access Power NI Perks, our exclusive rewards scheme that offers discounts on energy-efficient appliances and other great household savings.
You might be replacing an older fridge freezer, moving to a more efficient washing machine, or simply looking to cut your electricity use at home. Power NI Perks gives you a smart way to save while making your home more efficient.
Energy guides for you
Learn more about solar power and greener living with helpful energy advice.
Written by: Power NI Energy Experts



